About Ring Pump
With the development of the Ring Pump, Aquatech has succeeded in significantly extending the tube life,
which was a weak point of conventional tube pumps.
The features of the Ring Pump are explained below in comparison with the conventional tube pump.
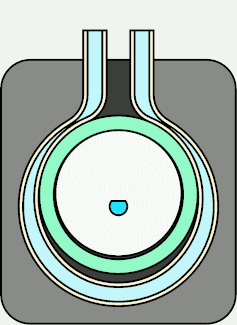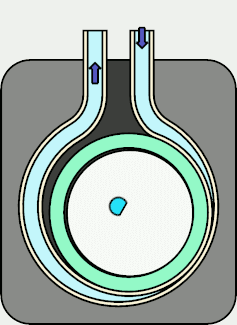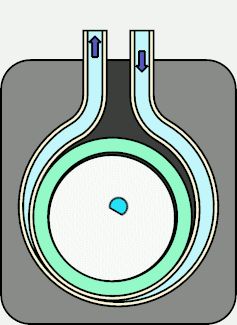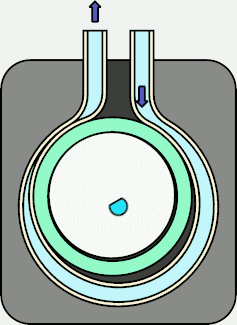
Structure and operation of Ring Pump

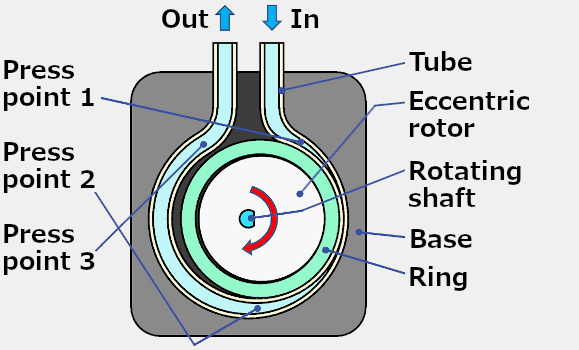
The Ring Pump consists of the following parts.
- Inverted Ω-shaped recessed base
- A tube inserted along the inside of the dent
- Cylindrical rotor with eccentric rotation center ("eccentric rotor")
- Ring inserted in the eccentric rotor
- Motor mounted on the back of the base. The rotation center of it is aligned with the center of the cylindrical part of the Ω-shaped recess.
- A lid for storing the tube, eccentric rotor, and ring (the figure above shows the state without the lid).
The ring pushes the tube at the point where the eccentricity of the eccentric rotor is maximized
(on the right side of the axis of rotation in the figure).
With this configuration, when the motor is rotated clockwise (in the direction of the arrow),
the motor moves as shown in the animation on the right, and the press section repeats the movement
of "Press point 1" → "Press point 2" → "Press point 3".
When the motor rotates and the compression point moves, the suction side of the compressed tube returns to its original shape due to the elastic force.
Therefore, the pressure in that part becomes low and the liquid is sucked in.
On the discharge side, the liquid is squeezed out and discharged as the compression point moves.
Comparison with conventional tube pump (roller pump)

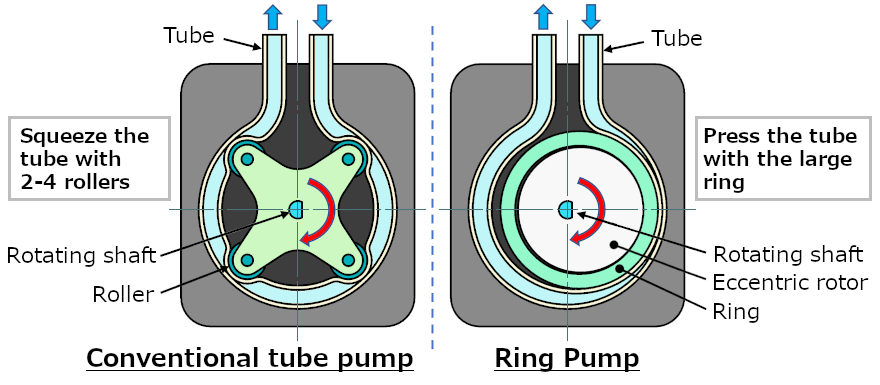
Conventional tube pumps use multiple small diameter rollers to squeeze the tube.
The Ring Pump uses a mechanism that gently presses the tube with the large-diameter ring.
Due to the above structure
- Conventional tube pumps press the tube with small diameter rollers, causing the tube to deform rapidly.
In comparison, the Ring Pump pushes with a large diameter ring, which gently deforms the tube.
- Conventional tube pumps require multiple rollers (for example, 4 in the figure above),
so the tube is pushed multiple times in one revolution (4 times in the figure above). The Ring Pump reduces the strain on the tube because the tube is pushed only once per revolution.
- The stress on the tube also affects its inner surface, and as the operating time increases, fragments pulverized by compression and friction are generated. The ring pump, which exerts less stress on the tube, generates fewer wear particles compared to conventional tube pumps.
(You can download our experimental data on the generation of wear particles. Click here to download.)
For these reasons, the Ring Pump has succeeded in extending the life of the tube.
Features of Ring Pump

The Ring Pump realizes many advantages due to its unique structure
- The tube-friendly design extends the life of the tube.
- The simple structure makes it suitable for miniaturization. We have also an ultra-compact pump (RP-TX series) with a discharge rate of 30 nL/min.
- Since the Ring Pump has a structure that always closes the tube, it has a check valve effect.
However, the check valve effect may not be perfect depending on the pressure on the discharge side, so it is recommended to use a check valve.
- Due to the structure that constantly closes the tube, it has a self-priming effect and does not require priming.
- Two or three connected pumps are also available. They are possible to reduce pulsation.
We have commercialized the RP-2S / RP-2GⅡ series as standard models.
- Various liquids can be sent by selecting the appropriate tube material.
If you provide the liquid to be used, we will perform a chemical resistance test on the tube to assist in selecting the appropriate tube.
Equipment using Ring Pump

Pumps are rarely seen from the outside, but are used in many places around us.
Below are examples of equipment and applications that use our Ring Pumps.
| Field |
Examples of equipment and applications |
| Beverages, food related |
Reduced water generator
Soup stock supply machine
Cup coffee vending machine
|
| Cleaning related |
Laundry
Car wash machine
Floor cleaning machine
Electric toilet seat
|
| Printer |
Large professional-quality printing machine |
| Aquaculture / cultivation related |
Hydroponics
Seafood aquaculture
|
| Medical and nursing related |
Dialysis machine
Nursing care bathtub
Hand disinfection equipment
|
| Industrial |
Cutting oil / press oil supply machine
Constant humidity chamber
|
| Laboratory |
Cell culture
Biotechnology
Regenerative medicine
Micro-TAS
|
| Universe |
Experimental equipment at the space station |